Injection Molding 11 Big Elements Explained
11 Elements of Injection Molding
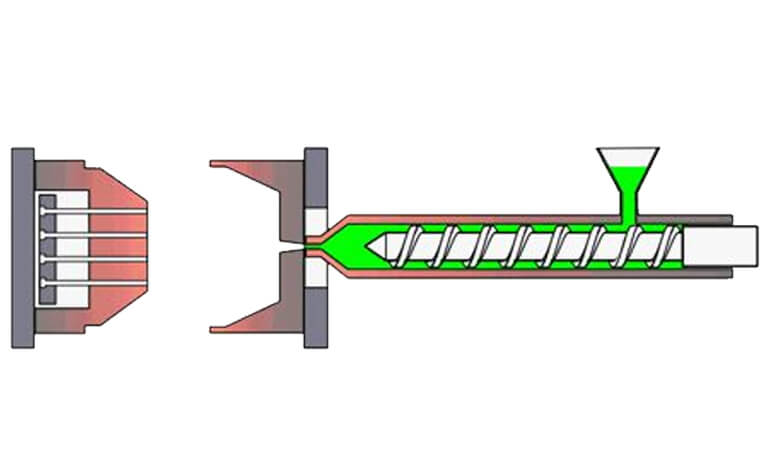
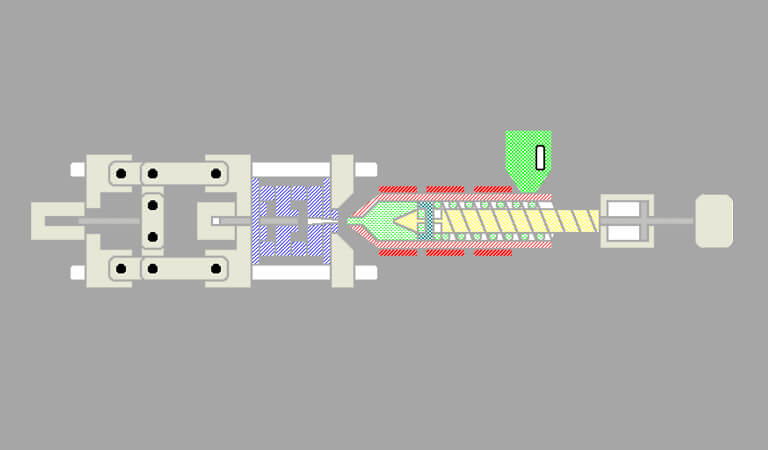
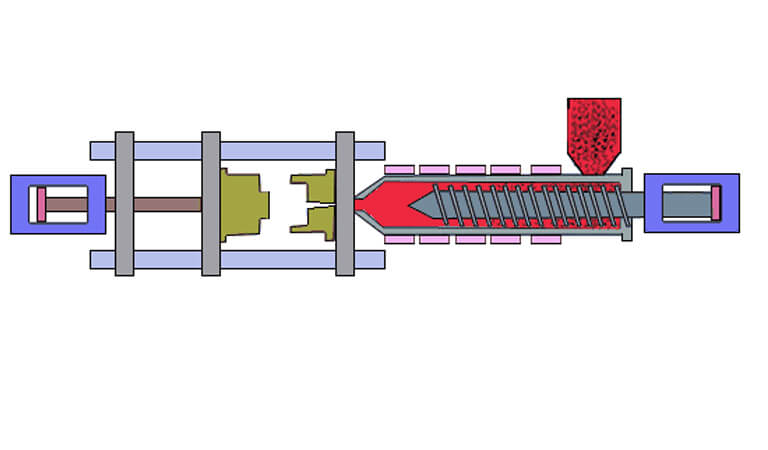
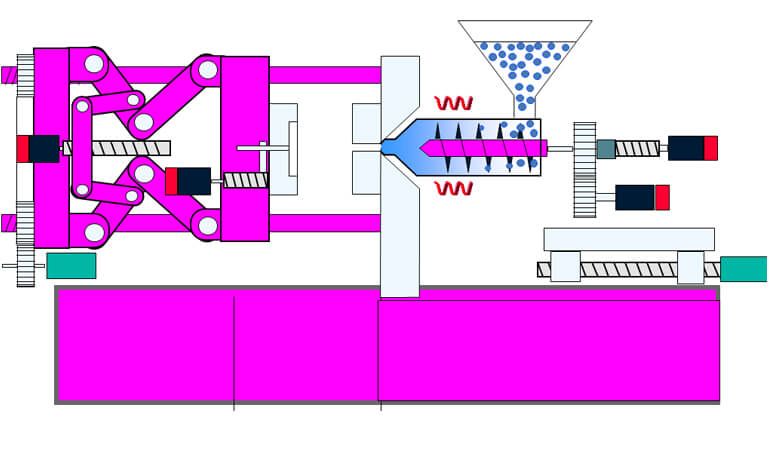
The purpose of injection molding is to transform the raw materials of thermoplastics into products that can be used and maintain their original properties through the important process conditions of injection molding. Therefore, the preparation of injection molding process parameters is an important part of the injection molding process.
1、injection molding temperature control: injection molding process needs to control the temperature of the barrel temperature, nozzle temperature and mold temperature. The main purpose of barrel temperature and nozzle temperature control is to make the material in the barrel fully plasticized and flowing.
2、The purpose of the mold temperature control is: to make the molten material in the process of filling the mold to improve a certain degree of fluidity, to help the molten material can quickly fill all parts of the mold cavity. Secondly, it also makes the material filled with mold cavity to the fixed temperature can be fully cooled and shaped. Third, the mold temperature control has a great impact on the intrinsic properties and apparent quality of the product.
3、Pressure control: During the processing of injection molded products, the pressure needs to be controlled including injection pressure and plasticizing pressure (i.e. back pressure).
4、Injection pressure: The pressure is transmitted to the end of the barrel through the hydraulic system of the injection machine (electric injection machines use servo motors) to push the screw forward, that is, the pressure applied to the end of the screw is called injection pressure.
In injection molding, the injection pressure plays a role in overcoming the flow resistance of the molten plastic from the barrel to the mold cavity, filling process, giving the rate of molten mold filling and compaction of the molten material.
5、plasticizing pressure: refers to the top of the screw melt in the screw rotation back by the pressure called plasticizing pressure, also known as back pressure.
Can also be said to overcome the screw into the material when the resistance generated by the rotation of the back pressure.
In general, the appropriate increase in back pressure can make the melt temperature uniform, uniform mixing of color, but also can discharge the gas in the melt, the normal production operation, the size of the back pressure should be in the premise of maintaining the quality of the product the smaller the better.
6、Time control: The time that needs to be controlled during the injection molding process includes: injection time, holding time, plasticizing time, cooling time, and cycle time.
7、Injection time: The time required for the molten material in the barrel to basically fill the cavity under injection pressure is called the injection time.
8、Pressure-holding time: It is the time to apply pressure to the plastic in the cavity. However, it should be noted that before the melt is frozen at the gate, the length of holding time has an effect on the dimensional accuracy of the product, but it has no effect if the melt is frozen at the gate.
9, plasticizing time: from the screw began to rotate into the material, until the set metering position required time called plasticizing time, the length of time directly affected by the back pressure and screw speed. It must be noted that the plasticizing time must be completed within the cooling time.
10、Cooling time: Cooling time refers to the time required for the plastic melt to be completely formed at a fixed temperature after the cavity is filled. The length of the cooling time mainly depends on the thickness of the product size, but also to ensure that the product does not cause changes in the principle of demolding.
11、Cycle time: Cycle time is the time required from the start of mold closing of the injection machine to the end of product demolding. The cycle time includes several times mentioned earlier, i.e. injection time, holding time, cooling time (cooling time includes plasticizing time).
The length of cycle time is related to the reasonable setting of process parameters. It is also related to whether the production process is continuous and automated.