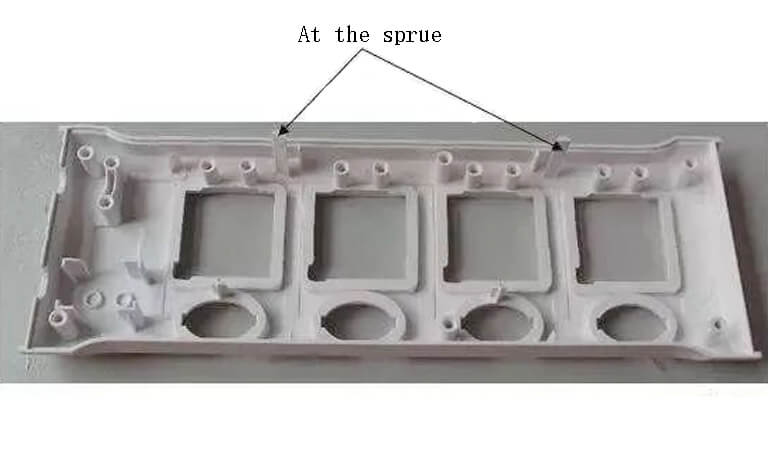
Causes of poor gate cutting - 3 major countermeasures
This is a phenomenon where the gate connecting the formed product, the main flow channel and the manifold is not easily cut off when forming with a point gate etc. If a point gate or a latent gate is chosen, the gate connecting the formed product, the main flow channel and the manifold will automatically break off while the mould is opened. However, if the shape or size of the gate is not suitable, it will produce a poor cut of the gate and remain inside the mould
ll、Second, the generation of poor gate cutting causes
1、Poor balance in terms of forces
To ensure that the product part is cut off from the manifold part at the gate, it is important to maintain a balance between the three forces of "gate strength", "manifold holding force" and "product holding force". It is very important to maintain a balance between the three forces of "gate strength", "manifold retention" and "product retention".
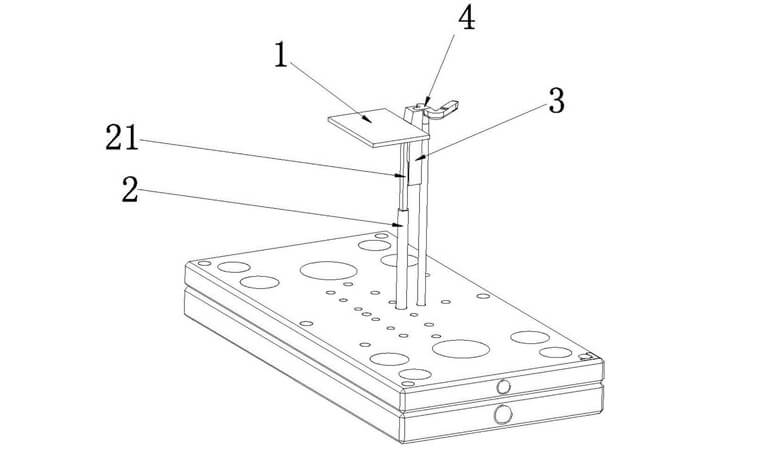
When the mould is opened, if the manifold part is left on the fixed side and the product part on the movable side, both will be cut off at the gate. If the gate is too strong or if the product part has a weak retention force with the manifold, the gate will not cut properly.
Generally, the manifold is held by a locking pin; the holding force depends on the shape and size of the pin and the temperature of the manifold section when the mould is opened. If the locking pin is not of sufficient size or slope, the gate will fall off before it is cut, so rather than increasing the strength of the gate, it is better to increase the retention of the manifold.
Conversely, too much holding force in the manifold will prevent the manifold from being released from the mould. Also the strength and rigidity of the resin will vary with temperature, so this must also be adjusted for.
The product is held in part by the friction of the lateral slope, or slip core. In cases where the product is held by the friction of the slope, it must still reach above the gate strength. This is also subject to the influence of temperature.
In addition the gate strength is of course influenced by the gate design. If the gate size is large, the strength will increase and thus the gate will not be easily cut. In the case of a 2-piece formwork with a tunnel gate, this is also influenced by the angle and position of the gate. In the case of a 3-piece formwork with a point gate, this is also influenced by the slope of the 2 main flow channels, grinding etc.
(1) Mould temperature
Influenced by the temperature of the resin after cooling. If the resin temperature changes, the strength and stiffness will also change.
(2) Holding pressure and holding time
Influenced by the amount of resin filling, the product, the size of the main flow channel and the manifold. Their size has a significant influence on the retention of the slope friction on the sides. When the size is too large it can even be impossible to release the mould.
(3) Injection speed
Influenced by the amount of resin filling, the product, the size of the main flow channel and the manifold.
2、Problems inherent in rank
In the case of impact resistant grades or alloys, for example, resins with elastomers have a slower cure rate and a lower modulus of elasticity, making them more susceptible to poor gate cutting than other materials. This means that countermeasures need to be fully investigated at the mould design stage
lll、Countermeasures for poor gate cutting
Changing the intensity balance
Adjust the moulding conditions for poor gate cutting as follows
When the manifold is left on the moveable side
It can be attributed to the weakness of the manifold locking pin on the fixed side, or the high strength of the gate section. Countermeasures can therefore be taken to increase the holding strength of the manifold locking pin, or to reduce the strength of the gate. Modifying the mould to change the size of both is also an option.
If the forming conditions are to be changed, methods to reduce the mould temperature, promote curing around the manifold locking pin and increase strength may also be effective. In the case of a tunnel gate, a correction to the gate section may also be considered.
When the manifold is left on the fixed side
This can be attributed to a weak lateral slope of the product part or a strong gate part. One remedy is to modify the mould to strengthen the slope or reduce the gate. Another solution is to increase the holding pressure and to increase the size of the manifold to improve the holding force.
When the product and manifold are left on the centre plate in a 3-piece mould
There is a high probability of the gate being too strong, so the gate size should be slightly reduced, or conversely the manifold locking pin should be strengthened. In terms of forming conditions, reducing the holding pressure may also be effective.